Table of Contents
SDK Components
The SDK is divided into logical components to separate responsibilities and create interfaces that you can re-implement using custom tools such as hardware accelerators.
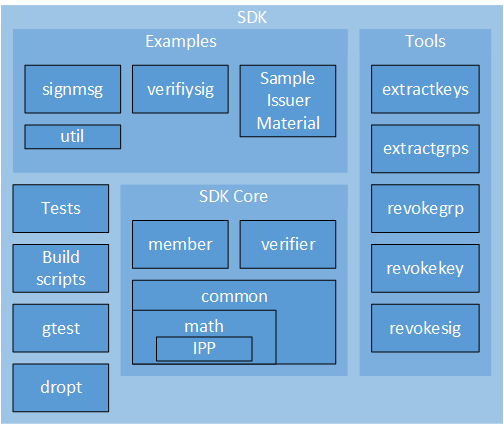
The Intel® EPID SDK is divided into the following components:
SDK Core
Components in the SDK Core implement the features of Intel® EPID.
| Component | Description ------------— |
|---|---|
| member | Library containing APIs needed to implement a member |
| verifier | Library containing APIs needed to implement a verifier |
| common | Library containing common types and functions |
| math | Math primitives used by member and verifier |
Samples
The SDK includes Test Data in example/data that is intended to be provisioned in members and verifiers so that they can operate without real issuer material. (For information on how to work with real issuer material, refer to Managing Groups with iKGF.)
The SDK also includes signing and verification Examples that show how to use the SDK APIs in working code.
| Component | Description ------------— |
|---|---|
| signmsg | A sample program showing how to sign messages |
| verfifysig | A sample program showing how to verify signatures |
| util | Common utilities used by samples |
| Sample Issuer Material | Sample keys and revocation lists |
Tools
The SDK provides tools to interact with Intel® EPID related services such those offered by the Intel® Key Generation Facility.
| Component | Description ------------— |
|---|---|
| extractgrps | A tool to extract groups from a bulk group file |
| extractkeys | A tool to extract member keys from a bulk key file |
| revokegrp | A tool to create a revocation request for a group |
| revokekey | A tool to create a revocation request for a member key |
| revokesig | A tool to create a revocation request from a signature |
Other Components
The SDK comes with a number of other components that support building and validating the code.
| Component | Description ------------— |
|---|---|
| gtest | gtest unit test framework |
| Build Scripts | Scripts to configure and build the SDK |
| dropt | Library for parsing command line |
Math primitives are implemented in the math sub-component of common. The reference math primitive implementation is based on a non-optimized Vanilla C subset of the Intel® Performance Primitives. Math is designed so that you can replace its implementation to call custom hardware IP blocks or optimized libraries.
Intel® EPID 1.1 Compatibility
In addition to the default Intel® EPID 2.0 APIs, the verifier component also includes APIs that allow verification of Intel® EPID 1.1 signatures.
Billions of existing devices, including most Intel platforms manufactured since 2008, create signatures that need Intel® EPID 1.1 verification.
For details on verifying Intel® EPID 1.1 signatures see Intel® EPID 1.1 support in the API Reference.
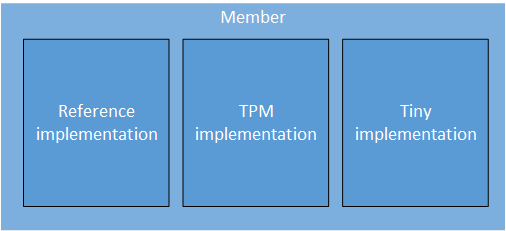
Member Implementations
There are three member implementations. You can use a specific compilation option to select the implementation that will be used at compile time. The implementations are:
- Reference: This default implementation gives guidance on partitioning member operations between highly sensitive ones that use the
fvalue of the member private key, and less sensitive ones that can be performed in a host environment. To build in default mode, refer to Building from Source. - TPM: This TPM member implementation uses the TPM for signing by linking to the IBM TSS. To build in TPM mode, refer to Building the SDK in TPM Mode.
- Tiny: This tiny implementation builds the SDK with a substantially reduced code size. To build in tiny mode, refer to Optimizing for Code Size.
Folder Layout
The Intel® EPID SDK has two filesystem layouts: the Source Layout and the Install Layout.
The Source Layout is what you find when you download the SDK and extract it to disk. This layout contains all of the files that you need to build the libraries, samples, tests, and data generated by the SDK.
The Install Layout is the layout of files under the _install folder after you build the SDK.
Source Layout
The Source Layout is used by the build scripts in the Intel® EPID SDK to find components and files needed to create libraries and executables.
epid-sdk/
|__ LICENSE.txt Distribution license
|__ NOTICE.txt Legal notices
|__ README.md Readme
|__ CHANGELOG.md Change log
|__ SConstruct Parts based build configuration
|__ configure Make based build configuration
|__ Makefile.in Make based build configuration
|
|__ doc/
| |__ html/ HTML format documentation
| |__ index.html Entry point for HTML format documentation
|
|__ epid/
| |__ common/ Source for Common
| |__ common-testhelper/ Source for unit test helper common helpers
| |__ member/ Source for Member
| |__ verifier/ Source for Verifier
|
|__ example/
| |__ data/ Binary data used for testing and tutorials
| |__ compressed_data/ Compressed Member Key Binary data used for testing and tutorials
| |__ signmsg/ Source for message signing example
| |__ util/ Common utilities for examples
| |__ verifysig/ Source for signature validation signing example
|
|__ ext/
| |__ dropt/ Third party library for parsing command-line options
| |__ gtest/ Third party gtest library
| |__ ipp/ Intel(R) Performance Primitives library
|
|__ parts-site/ Parts platform config scripts
|
|__ tools/
|__ extractgrps/ Tool to extract groups
|__ extractkeys/ Tool to extract keys
|__ revokegrp/ Tool to create group revocation request
|__ revokekey/ Tool to create a member key revocation request
|__ revokesig/ Tool to create a signature based revocation
request
Install Layout
The Install Layout contains the data developers need to develop and build their applications using the Intel® EPID SDK. Once built, the Install Layout has no dependency on the Source Layout, allowing developers to build the SDK once and reuse the built files in other locations or on other computers.
_install/
|__ epid-sdk/
|__ include/ C include header files for the SDK
|__ lib/
| |__ <platform> Target specific static libraries for the SDK
|
|__ example/ Sample applications and data
|__ compressed_example/ Compressed Member Key Binary data for sample applications
|__ test/ Unit test executables (if unit tests built)
|__ tools/ Tools